Additional Cancer Risk Genes
APC
Associated with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon Cancer
Additional cancer risks: desmoid tumors, hepatoblastoma, a retinal condition called CHRPE, thyroid cancer, bone tumors (osteomas), and upper bowel polyps
No association to prostate cancer at this time
Screening and Management
Colon cancer: Individuals with APC mutations should begin screening with colonoscopies at a young age (10-15 years) and have them done yearly. As people get older, complete removal of the colon may be recommended.
There are also recommendations for screening to reduce the risk of the other cancers that can occur in people with FAP or attenuated FAP. Talk to your doctor about these additional recommendations.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.
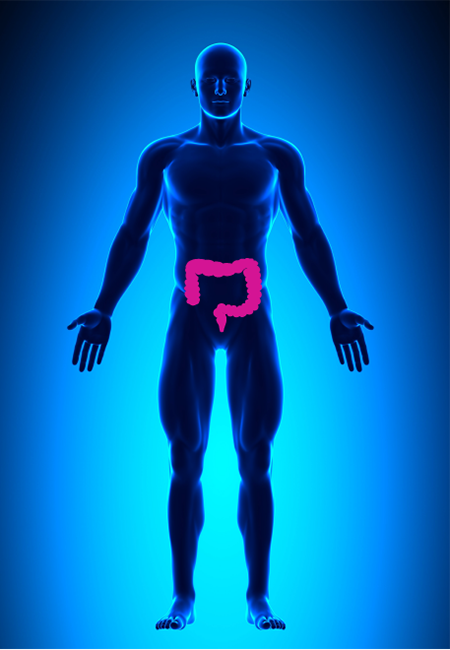
Images reflect cancers relevant to men only, additional cancer risks not shown
AXIN2
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon Cancer
No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Colon cancer: Mutations in this gene have been associated with colorectal cancer as well as lack of proper formation of teeth. There are no current recommendations for screening for colorectal cancer based upon AXIN2 mutations. Colon cancer screening recommendations are usually based upon personal and family history.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
BAP1
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Melanoma (eye and skin), Mesothelioma (lining of lungs), Kidney Cancer
Screening and Management
Eye melanoma: Individuals with BAP1 mutations are recommended to see an ophthalmologist for detailed eye exams.
Skin melanoma: Recommendation to see a dermatologist for yearly (or more frequent) skin exams
Mesothelioma: No current screening guidelines exist. Patients can talk to their doctors about options for imaging or trials.
Kidney cancer: No current screening guidelines exist, though imaging may be considered. Talk to your doctor about options.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.
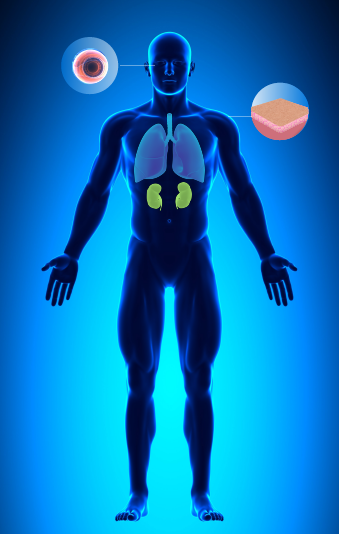
Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
BARD1
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Neuroblastoma
For Women: Risk of ovarian cancer and breast cancer.
Screening and Management
Prostate cancer: Men with metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer may be considered for targeted therapy
Breast and ovarian cancer: There are no current recommendations for cancer screenings based on the BARD1 mutation. Recommendations are based on personal and family history.
Neuroblastoma: There may be consideration to have yearly neurologic exams.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
BLM
Cancer Risks
Associated with Bloom Syndrome
For Men and Women: Colon Cancer
For Women: Female Breast Cancer
No association to prostate cancer at this time
Screening and Management
There are no current recommendations for cancer screenings based on BLM mutations. Screening recommendations are based upon personal and family history.
Reproductive: There are no current recommendations for cancer screenings based on BLM mutations. Screening recommendations are based upon personal and family history.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
BMPR1A
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon Cancer
No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Colon Cancer: Associated with juvenile polyposis syndrome. Screening for colorectal / colon cancer is recommended to begin around the age of 15, with ongoing screening.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
BRIP1
Cancer Risks
For Women: Ovarian Cancer
For Men: No current increase in prostate cancer risk known.
Screening and Management
Prostate cancer: Men with metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer may be considered for targeted therapy.
Ovarian Cancer: Current recommendations include consider removal of the ovaries at age 45-50.
Additional recommendations are based upon personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
CDH1
Cancer Risks
Stomach cancer (men and women), breast cancer (women only)
No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Breast Cancer: An annual mammogram is recommended, possibly considering breast MRI at age 30. Risk-reducing mastectomy may be considered based upon personal and family history.
Stomach Cancer: Due to the high risk of stomach cancer, discussion of removal of the stomach is conducted.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
CDK4/CDKN2A
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Pancreatic cancer, melanoma
No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Melanoma: Full body skin exams every 6-12 months.
Pancreatic Cancer: There are no current recommendations for pancreatic cancer, though imaging of the pancreas is available. Individuals may consider discussion with a high-risk gastroenterologist.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.
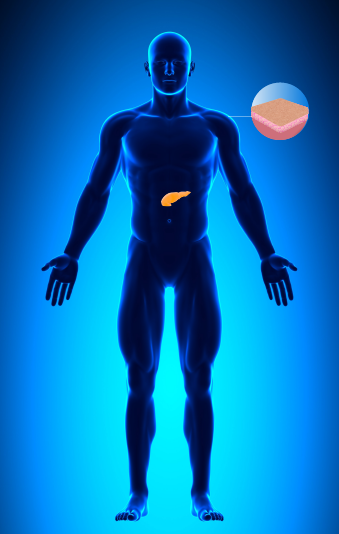
Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
GREM1
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon Cancer
No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Colon Cancer: Colonoscopy is recommended starting at age 25-30.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
MUTYH
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon Cancer
For Men: No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Colon Cancer: Colonoscopy recommendations are based on the mutation status and family history of colon cancer. First colonoscopy may be recommended beginning at age 40 or 10 years prior to a first-degree relative’s age of colorectal cancer and continued every 5 years.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
POLD / POLE
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon Cancer
For Men: No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Colon Cancer: Colonoscopy is recommended to begin at age 25-30 and proceed according to findings.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
PTEN
Associated with Cowden syndrome
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Thyroid Cancer, Colon Cancer, Kidney Cancer, and Melanoma;
For Women: Uterine Cancer, Breast Cancer
No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Breast Cancer: Screening may be recommended beginning at age 30-35. Addition of breast MRI to mammogram can also be considered.
Thyroid Cancer: Annual thyroid ultrasound can be recommended from childhood.
Colon Cancer: Colonoscopy can be recommended starting at age 35.
Kidney Cancer: Renal ultrasound may be recommended at age 40.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.
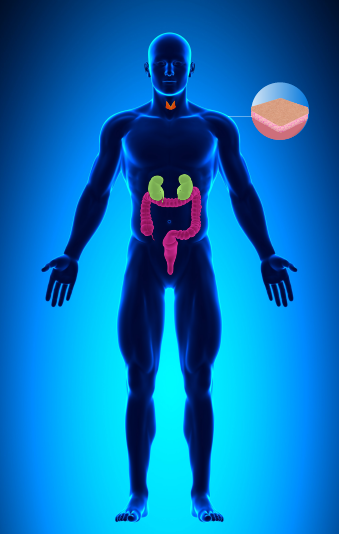
Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
RAD50/RAD51C/RAD51D
Cancer Risks
For Men: No current increase in prostate cancer risk known.
For Women: Ovarian Cancer
Screening and Management
Prostate cancer: Men with metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer may be considered for targeted therapy.
Ovarian Cancer: Removal of the ovaries may be considered at age 45-50.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
SMAD4
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon cancer
No association to prostate cancer at this time
Screening and Management
Colon Cancer: Colorectal cancer screening is recommended beginning at age 15, with ongoing screening based on polyp findings.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
SMARCA4/SMARCB1
Cancer Risks
For Men: No association to prostate cancer at this time.
For Women: Breast cancer
Screening and Management
Breast Cancer: There are currently no guidelines for breast cancer screening based upon mutations on these genes.
Recommendations are based upon a patient’s personal and family history.

Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
STK11
Cancer Risks
For Men and Women: Colon cancer, stomach, pancreas, small intestine.
For Women: Breast Cancer, Ovarian cancer (sex cord type)
For Men: Testicular Cancer
No association to prostate cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
Colon Cancer: Colonoscopy every 2-3 years starting in the teen years.
Breast Cancer: Mammogram and breast MRI is recommended annually starting at age 25.
Ovarian Cancer: Pelvic exams and transvaginal ultrasound may also be performed starting in the teen years.
Testicular Cancer: Annual testicular exam starting at age 10.
Pancreatic Cancer: MRCP or endoscopic ultrasound every 1-2 years starting age 30-35 may be considered.
Stomach Cancer: Upper endoscopy starting in the late teens.
Small intestinal Cancer: Upper endoscopy starting at age 8-10.
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history.
Images reflect cancers relevant to men only
TP53
Cancer Risks
Associated with Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
For Men and Women: Sarcomas, brain tumors, and adrenocortical carcinoma; multiple other cancers may also be associated, including hematologic malignancies, female breast cancer typically at very young age.
No clear association with Prostate Cancer at this time.
Screening and Management
It is important for a patient with a TP53 mutation to be followed in a specialty clinic with expertise in Li-Fraumeni syndrome management. Multiple screening tests and imaging are needed starting at young ages. A few of the cancers and screening are shown below, but many other recommendations also exist:
Breast Cancer: Screening is recommended beginning at age 20-29. Can discuss risk-reducing mastectomy.
Colon Cancer: Colonoscopy recommended starting at age 25.
For other cancer risks: Annual whole body MRI
Brain tumors: Annual brain MRI
Additional recommendations are based upon a patient’s mutation, personal and family history
